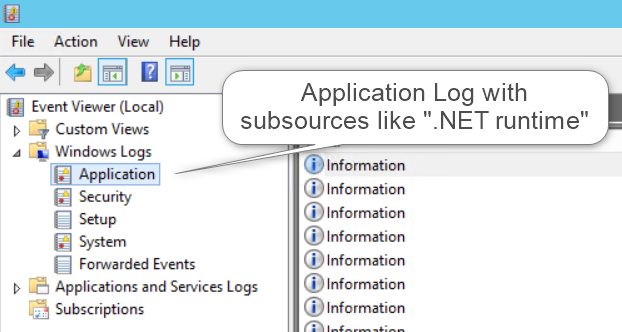
Write a windows EventLog entry
If you want wo write to a local Windows EventLog in your C# application, you can use the following methods to write your custom entry into a log source.
For writing to the Application log and its sub sources, you don’t need to run your application with administrator privileges. But if you want to create your own sub source, with the name of your application for example, you need more rights, because the act of creating it has to search through the other logs and sources to be sure that yours is unique. Furthermore, Microsoft recommends creating a new source before logging to it because of system caused delays.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public static class EventLogWriter
{
private const string EventLogApplicationSubSource = ".NET Runtime";
private const int EventLogDefaultId = 1026;
/// <summary>
/// Writes a given message to the Application Windows EventLog.
/// The optional parameters can be overwritten with custom values.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">message to be written as log entry</param>
/// <param name="eventLogEntryType">overwrites the default type of Information to a custom set type</param>
/// <param name="sourceName">Overwrites the default ".NET Runtime". Custom values have to exist, or this throws an exception.</param>
/// <param name="eventId">OVerwrites the default id of 1026 to a custom id. keeping the default is recommended, else chose an id above 1000</param>
public static void WriteApplicationEventEntry(
string message,
EventLogEntryType eventLogEntryType = EventLogEntryType.Information,
string sourceName = EventLogApplicationSubSource,
int eventId = EventLogDefaultId)
{
using (EventLog eventLog = new EventLog())
{
eventLog.Source = sourceName;
eventLog.WriteEntry(message, eventLogEntryType, eventId);
}
}
}
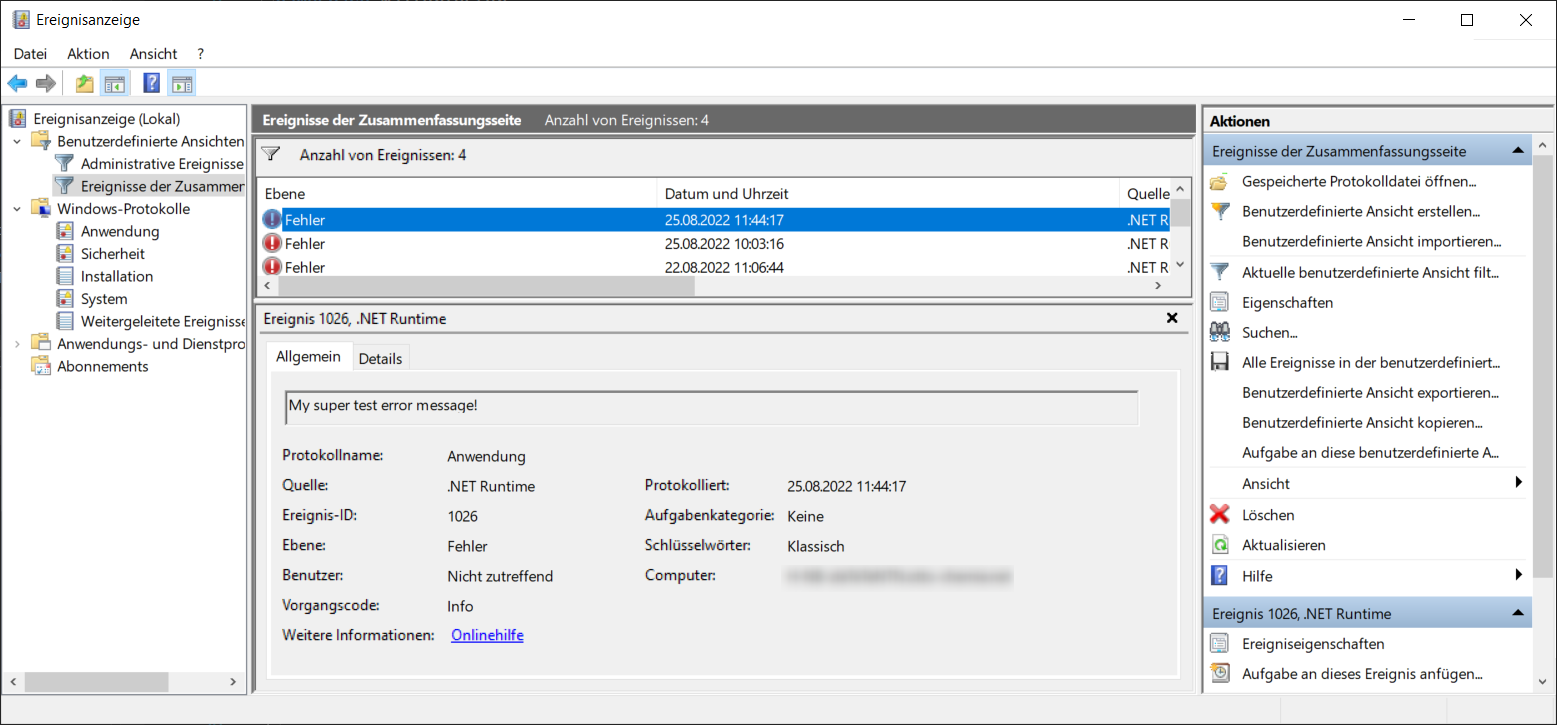
Calling this method with EventLogWriter.WriteApplicationEventEntry("My super test error message!", System.Diagnostics.EventLogEntryType.Error); will (kind of quick and dirty) write an entry with your message to the Application log. Keeping the default values will write it to the “.NET runtime” sub source. This will look something like this: