Windows Service (.NET Framework)
To create a Windows service to be installed and controlled in the services console you can create a console application project (Framework) with some extra classes. Another recommendation is to create an alternative startup for interactive mode, with which you can debug the service without having to install and uninstall it.
Project Properties
An example for a service with its properties:
Interactive Mode
This class shows a possible implementation of the interactive mode, with dependency injection, NerdBank Git Versioning, Serilog logging and stopping a console app with [Ctrl]+[C]:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
internal static class Program
{
private static bool _keepRunning = true;
/// <summary>
/// Host object with dependency injection registration
/// </summary>
public static IHost AppHost { get; set; }
private static void Main()
{
var serilogLogger = LogInitializer.CreateLogger(true);
Log.Logger = serilogLogger;
Log.Information("{ApplicationName} start", ThisAssembly.AssemblyName);
AppHost = ConfigureHost();
ServiceBase[] ServicesToRun;
ServicesToRun = new ServiceBase[]
{
new WindowsServiceEDU() // Your Service class here ...
};
if (Environment.UserInteractive)
{
try
{
RunInteractive(ServicesToRun);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Log.Error(ex, "An error occurred while running the service in interactive mode: {Message}", ex.Message);
throw;
}
}
else
{
try
{
ServiceBase.Run(ServicesToRun);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Log.Error(ex, "An error occurred while running the service: {Message}", ex.Message);
throw;
}
}
Log.Information("{ApplicationName} stop", ThisAssembly.AssemblyName);
Log.CloseAndFlush();
}
/// <summary>
/// Configures the host with registering the interfaces and class types.
/// Sets the Serilog logger as logging provider for typed ILogger injections.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>configured host to access its services</returns>
private static IHost ConfigureHost()
{
var host = Host.CreateDefaultBuilder()
.ConfigureServices((context, services) =>
{
// DI registry here ...
})
.UseSerilog()
.Build();
return host;
}
/// <summary>
/// Runs the application in interactive mode as console application instead of a win service.
/// </summary>
private static void RunInteractive(ServiceBase[] servicesToRun)
{
// Add handler for [Ctrl]+[C] press
Console.CancelKeyPress += delegate (object sender, ConsoleCancelEventArgs e)
{
e.Cancel = true;
_keepRunning = false;
Console.WriteLine("Received stop signal, will exit the application ...");
};
Console.WriteLine("Services running in interactive mode.");
Console.WriteLine();
MethodInfo onStartMethod = typeof(ServiceBase).GetMethod("OnStart", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
foreach (ServiceBase service in servicesToRun)
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting {0}...", service.ServiceName);
onStartMethod.Invoke(service, new object[] { new string[] { } });
Console.WriteLine("Started");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Press [Ctrl]+[C] to exit the application ...");
while (_keepRunning)
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine();
MethodInfo onStopMethod = typeof(ServiceBase).GetMethod("OnStop", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
foreach (ServiceBase service in servicesToRun)
{
Console.WriteLine("Stopping {0}...", service.ServiceName);
onStopMethod.Invoke(service, null);
Console.WriteLine("{0} Stopped", service.ServiceName);
}
Console.WriteLine("All services stopped.");
// Keep the console alive for a second to allow the user to see the message.
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
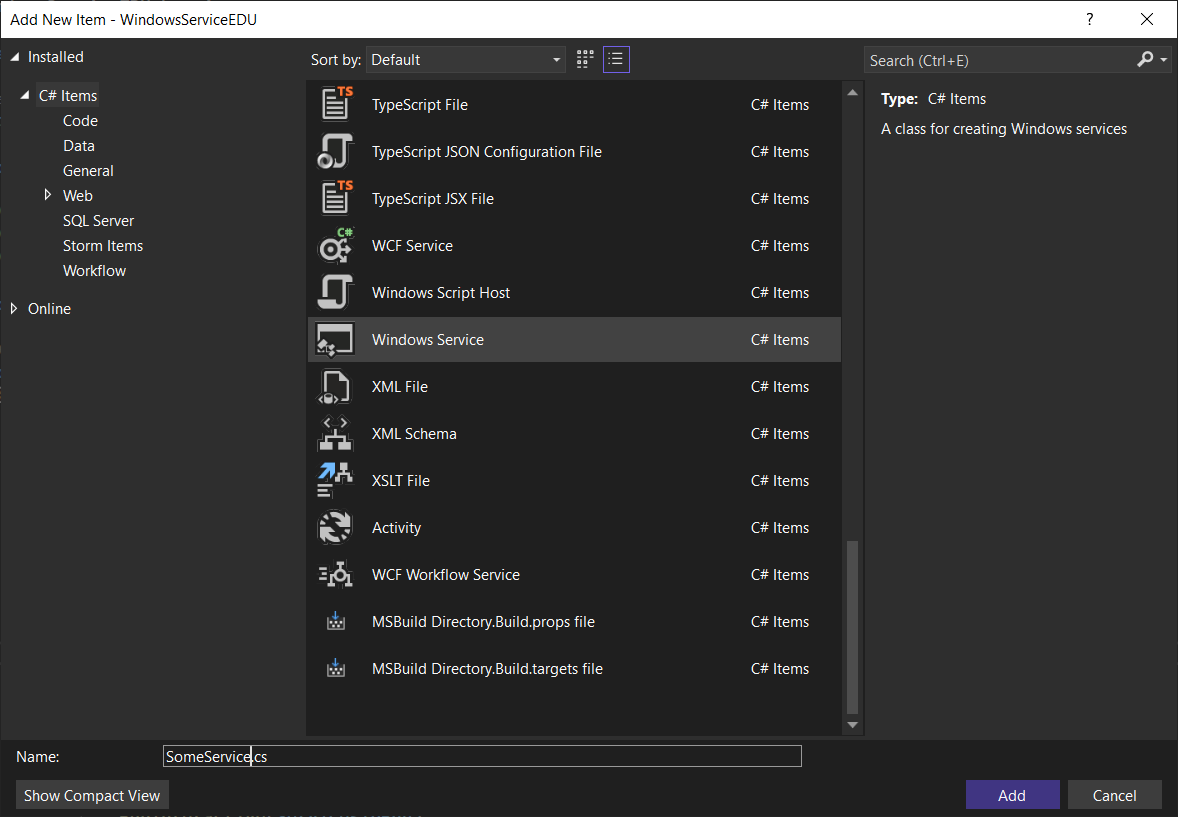
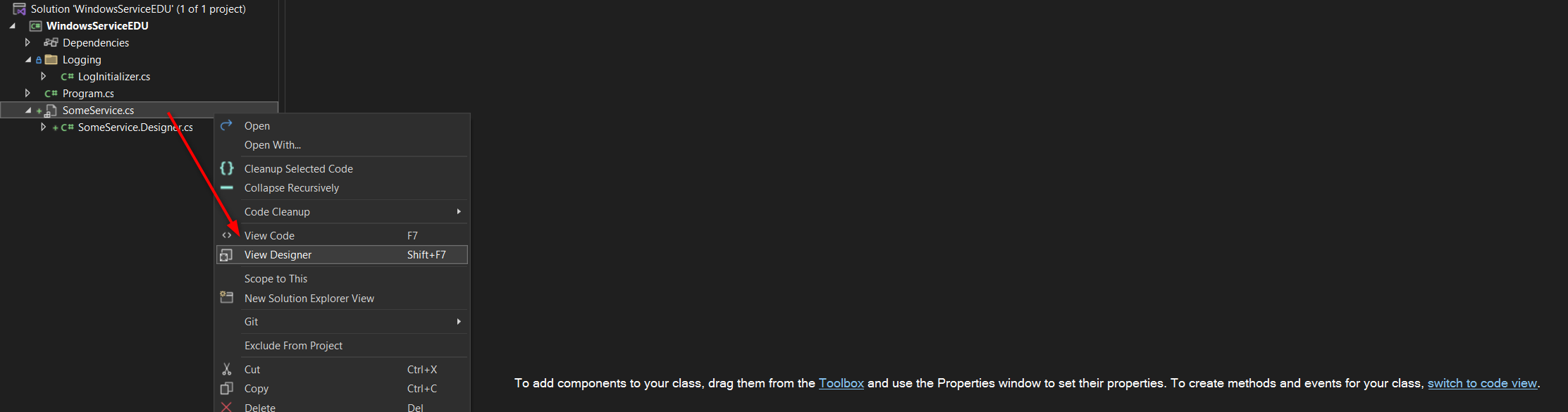
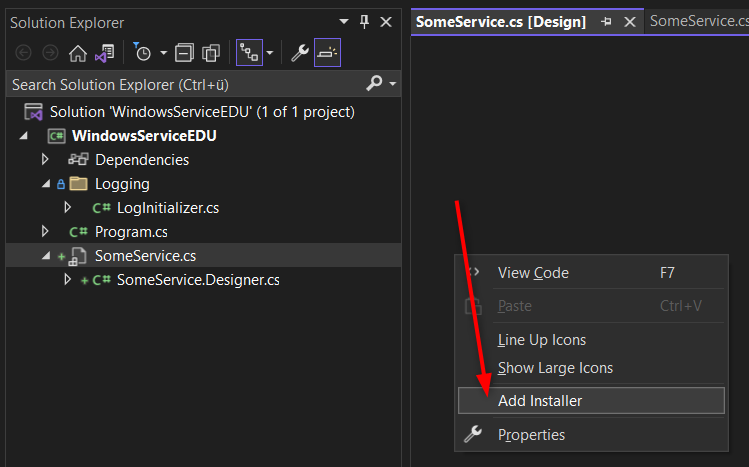
Service component and Installer
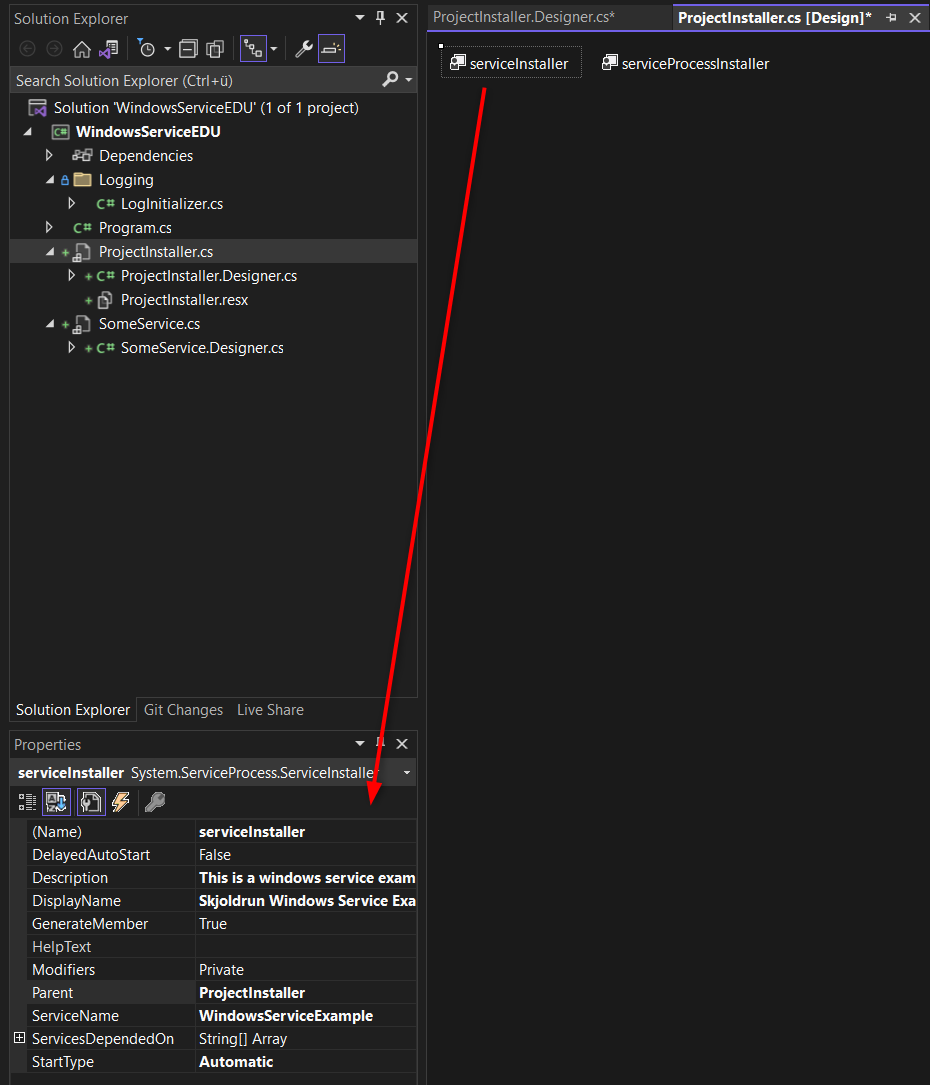
In newer VS editions there are no more Tools from the Toolbox available, so we have to do some tricks for adding the required classes, like the installer and its components. Open the Designer view and then Right Click the background to add the Installer:
Note: If you have created this project as console project for the newer .net and as SDK styled project right away, you might get some troubles for adding the serviceInstaller and the serviceProcessInstaller components. The sad thing is that I was not able to find any way to add the serviceInstaller and the serviceProcessInstaller components via the IDE, so I copied them from another project … 😒 So I recommend to setup the project as Framework project and then convert the project to the newer SDK style project file with Targetframework set to net48.
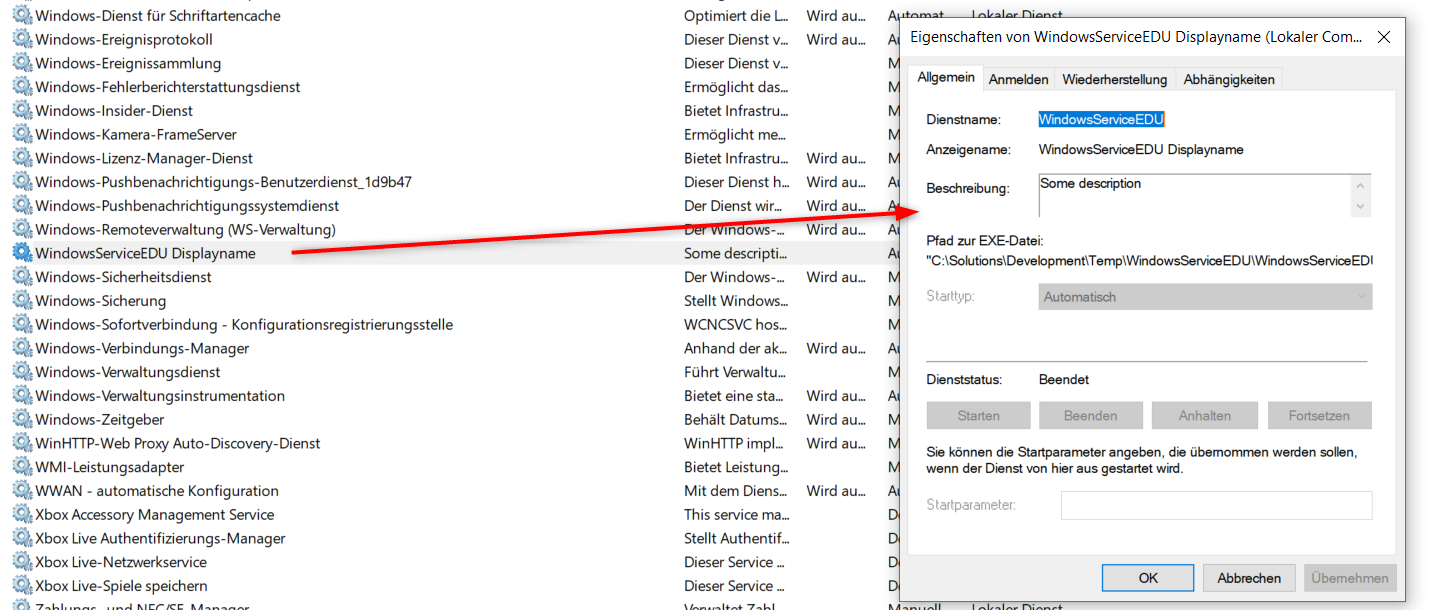
To configure the installer, you can now set some properties, like the name, the description or if the service will start automatically:
Convert to SDK Style project
I recommend to use the Try-Convert Tool. Then add the needed Package References and further reduce the csproj entries.
Install and Uninstall batch scripts
An easy way to install and uninstall the service is to have some batch scripts in the project folder.
Note: Call these from a console with Admin privileges. Installation and Uninstalltion can only be done by administrators of the machine.
Install.bat:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@ECHO off
REM Set the variables:
REM %sourcePath% to be the current directory path
REM %installUtilPath% for the .NET InstallUtil.exe
REM %serviceName% for the ServiceName
REM %serviceUser% for the ServiceUser
SET sourcePath=%cd%
SET installUtilPath="C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319"
SET serviceName=SomeService
SET serviceUser=SomeUser
REM Change to InstalUtils path
C:
CD %installUtilPath%
REM call InstallUtil to install the service
InstallUtil.exe /LogToConsole=true /username=%serviceUser% %sourcePath%\%serviceName%.exe
PAUSE
Uninstall.bat:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@ECHO off
REM Set the variables:
REM %sourcePath% to be the current directory path
REM %installUtilPath% for the .NET InstallUtil.exe
REM %serviceName% for the ServiceName
SET sourcePath=%cd%
SET installUtilPath="C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319"
SET serviceName=SomeService
REM Change to InstalUtils path
C:
CD %installUtilPath%
REM call InstallUtil to install the service
InstallUtil.exe /u /LogToConsole=true %sourcePath%\%serviceName%.exe
PAUSE
service console
Windows Service (.NET Core and newer)
There is a project template to create a so called worker service. This is able to run as Windows Service or as Linux deamon in the background. It contains a hosted service of a worker class by default, where the worker class has the work that should be repeated.
Project file
This is the csproj File without the Windows specific Service NuGet Package.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Worker">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net7.0</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<UserSecretsId>dotnet-WindowsServiceEDU.Net-b08ece4c-16b1-48f2-a099-b1e918138f2e</UserSecretsId>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices" Version="7.0.1" /> <!-- Package for installable Windows Service -->
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting" Version="7.0.1" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Extensions.Hosting" Version="7.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Settings.Configuration" Version="7.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Sinks.Async" Version="1.5.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Sinks.Console" Version="4.1.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Sinks.Debug" Version="2.0.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Serilog.Sinks.File" Version="5.0.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
To Install it as a Windows Service you also need the Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices Package.
Activate .UseWindowsService() for the Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) Method to get a installable Windows Service.
Interactive Mode
This project template is by default interactively startable and opens a console while debugging. It has all the features, like launchsettings, appsettings and more.
This example comes with dependency injection, NerdBank Git Versioning, Serilog logging and stopping the console app with [Ctrl]+[C].
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var config = AppSettingsHelper.GetAppConfigBuilder().Build();
Log.Logger = LogInitializer.CreateLogger(config);
IHost host = Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseWindowsService() // activate to get installable Windows Service
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
services.AddHostedService<Worker>();
})
.UseSerilog()
.Build();
host.Run();
Log.CloseAndFlush();
}
}
The Worker Class
The worker class has a endless loop with a cancellation token and a wait timer for repetition. The cancellation token will come from the OS controlling the service.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
public class Worker : BackgroundService
{
private readonly IConfiguration _config;
private readonly ILogger<Worker> _logger;
private int _workerIntervalInSec;
public Worker(IConfiguration config, ILogger<Worker> logger = null)
{
_config = config;
_logger = logger ?? NullLogger<Worker>.Instance;
_workerIntervalInSec = _config.GetSection("AppSettings").GetValue<int>("WorkerIntervalInSec");
}
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
// do something here ...
_logger.LogInformation("Worker running every {interval} sec in {Env} environment at: {time}",
_workerIntervalInSec, DateTimeOffset.Now, AppSettingsHelper.GetEnvVarName());
await Task.Delay(_workerIntervalInSec * 1000, stoppingToken);
}
}
public override Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Application {name} start", ThisAssembly.AssemblyName);
return base.StartAsync(cancellationToken);
}
public override Task StopAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Application {name} stop", ThisAssembly.AssemblyName);
return base.StopAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
Serilog Async file logging
Serilog can be configured to use asynchronous file logging. Check the code below or the LogInitializer class for examples of implementation:
LogInitializer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public static class LogInitializer
{
/// <summary>
/// Creates the logger with inline settings.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Logger with inline settings</returns>
public static Serilog.ILogger CreateLogger()
{
return new LoggerConfiguration()
.Enrich.FromLogContext()
.WriteTo.Async(a =>
{
a.File("logs/log.txt", rollingInterval: RollingInterval.Hour);
})
#if DEBUG
.WriteTo.Console()
.WriteTo.Debug()
#endif
.CreateLogger();
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates the logger with settings from appConfig and enrichments from code.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="appConfig">appConfig built from appsettings.json</param>
/// <returns>Logger with inline and app.config settings</returns>
public static Serilog.ILogger CreateLogger(IConfiguration appConfig)
{
return new LoggerConfiguration()
.ReadFrom.Configuration(appConfig)
.Enrich.FromLogContext()
.CreateLogger();
}
//...
}
Appsettings
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
{
"Serilog": {
"Using": [ "Serilog.Sinks.Console" ],
"WriteTo": [
{
"Name": "Async",
"Args": {
"configure": [
{
"Name": "File",
"Args": {
"path": "log\\log.txt",
"rollingInterval": "Hour"
}
}
]
}
}
],
"MinimumLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Override": {
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"System": "Warning"
}
}
}
//...
}
Installing and uninstalling the Service
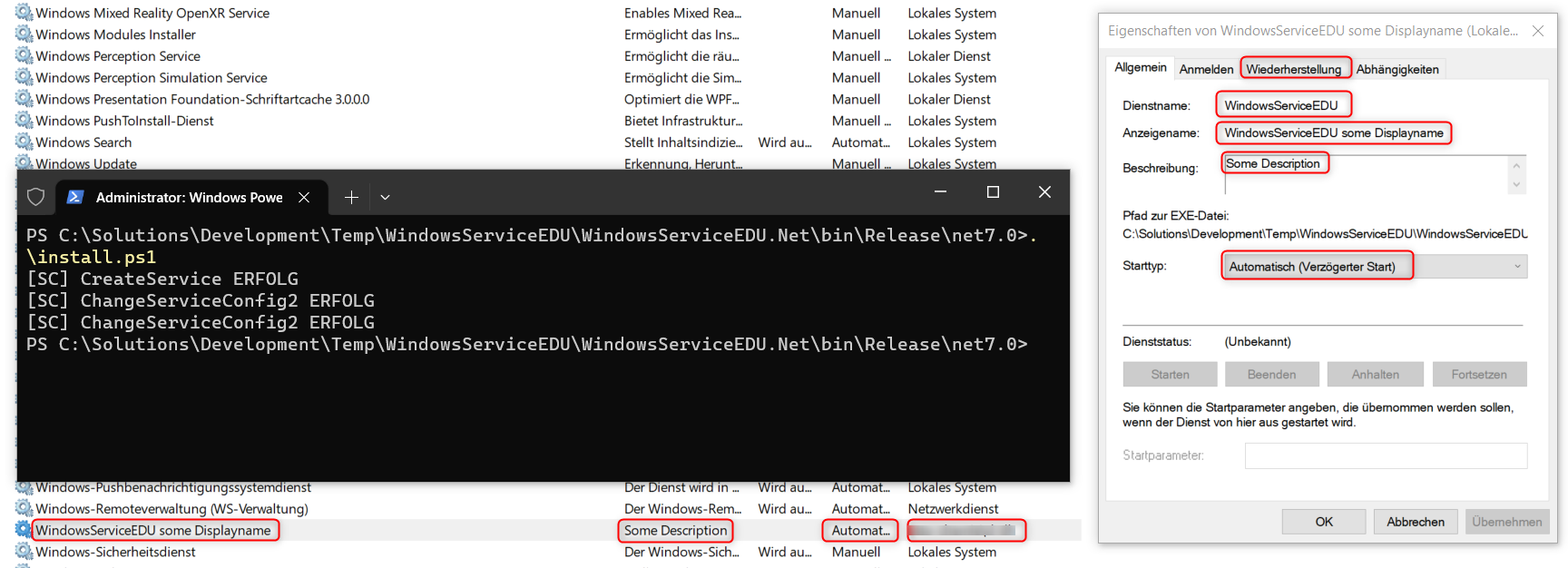
Installing and uninstalling the service can be executed via script, for example with PowerShell:
Install.ps1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# Installs a service with given configurations for user, path, restart etc.
# open a PowerShell Terminal with Administrator privileges
# sc.exe is needed in Powershell to not call teh sc commandlet for set content
$ServiceName = "WindowsServiceEDU"
$DisplayName = "WindowsServiceEDU some Displayname"
$Description = "Some Description"
$ServiceUser = "otto-chemie\cl-dh"
$StartUpMode = "delayed-auto" # possible are boot|system|auto|demand|disabled|delayed-auto
$Path = $PWD.Path # the path to the current directory
#Write-Host "Path to Service is: $($Path)\$($ServiceName).exe"
sc.exe create $ServiceName binpath= "$($Path)\$($ServiceName).exe" obj= $ServiceUser start= $StartUpMode
sc.exe description $ServiceName $Description
sc.exe failure $ServiceName reset= 30 actions= restart/5000 # Set restart options on failure
Uninstall.ps1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Deletes the service if not running any more, else mark for deletion after stop
# open a PowerShell Terminal with Administrator privileges
# sc.exe is needed in Powershell to not call teh sc commandlet for set content
$ServiceName = "WindowsServiceEDU"
sc.exe delete $ServiceName